Judaism Official Website

Welcome to the official guide to Judaism, a rich and ancient faith with a global reach. This comprehensive article aims to explore the diverse aspects of Judaism, from its historical roots and religious beliefs to its cultural impact and global community. With a focus on providing an engaging and informative experience, we delve into the intricacies of this remarkable religion, offering insights into its traditions, practices, and modern-day relevance.
The Historical Journey of Judaism: A Faith Rooted in Ancient Traditions

Judaism, one of the oldest monotheistic religions, traces its origins back to the ancient Near East. Its story begins with the patriarch Abraham, who is considered the founding father of Judaism. The faith emerged from the ancient Hebrew population, evolving over centuries and shaping the religious and cultural landscape of the region.
The Torah, the foundational text of Judaism, provides a historical and spiritual narrative, detailing the origins of the Jewish people and their covenant with God. This covenant, established through Abraham and later renewed with Moses, forms the basis of Jewish identity and religious practice.
Throughout history, Judaism has faced numerous challenges and transformations. From the Babylonian exile to the Roman conquest, the Jewish people have persevered, maintaining their religious and cultural identity despite adversity. This resilience is a testament to the strength and adaptability of Jewish faith and tradition.
The Evolution of Jewish Thought and Practice
Jewish thought and practice have evolved significantly over time, influenced by historical events, philosophical ideas, and cultural interactions. The Talmud, a central text in Judaism, reflects this evolution, offering interpretations and expansions of the Torah's laws and teachings. It represents a dynamic and ongoing dialogue within the Jewish community, shaping religious practice and ethical standards.
Jewish scholars and thinkers have contributed significantly to philosophical and theological discourse, exploring concepts of God, ethics, and human nature. Figures like Maimonides and Rabbi Akiva have left an indelible mark on Jewish thought, shaping the intellectual and spiritual landscape of Judaism.
| Jewish Scholar | Contribution |
|---|---|
| Maimonides | Authored the Mishneh Torah, a comprehensive code of Jewish law, and contributed significantly to Jewish philosophy, particularly in his Guide for the Perplexed. |
| Rabbi Akiva | A key figure in the development of the Mishnah, the first major written redaction of Jewish oral traditions. He also played a significant role in shaping Jewish ethics and law. |

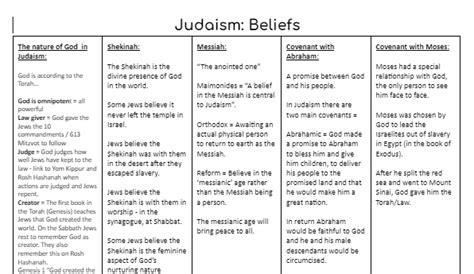
Core Beliefs and Practices: Unveiling the Heart of Judaism

At the core of Judaism lies a profound belief in one God, the creator and sustainer of the universe. This monotheistic belief forms the foundation of Jewish faith and practice, influencing every aspect of Jewish life and thought.
Judaism emphasizes the importance of living a righteous and ethical life, guided by the principles outlined in the Torah and the teachings of Jewish scholars. The concept of mitzvot, or commandments, provides a framework for Jewish behavior, covering a wide range of areas from personal conduct to societal norms.
The Significance of Torah and Prayer
The Torah, comprising the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, is central to Jewish belief and practice. It serves as a guide for living, detailing the history of the Jewish people and their relationship with God. Jewish study and interpretation of the Torah are ongoing, with new insights and applications emerging over time.
Prayer is an integral part of Jewish life, with set daily prayers and additional prayers for special occasions. These prayers, often recited in Hebrew, offer a means of connecting with God, expressing gratitude, and seeking guidance. The Sabbath, a day of rest and spiritual renewal, is a highlight of Jewish worship, marked by special prayers and traditions.
Rituals and Traditions: A Rich Tapestry of Jewish Life
Jewish life is rich in rituals and traditions, each carrying profound spiritual and cultural significance. From birth to death, these rituals mark significant life events and guide Jewish practice.
- Birth and Bar/Bat Mitzvah: The celebration of a child's birth and their coming of age, marked by a Bar or Bat Mitzvah ceremony, where they take on adult religious responsibilities.
- Marriage: Jewish weddings are steeped in tradition, with rituals like the chuppah (wedding canopy) and the breaking of the glass symbolizing the creation of a new family and the enduring nature of love.
- Sabbath and Festivals: The Sabbath, marked by rest and prayer, is a cornerstone of Jewish life. Jewish festivals, such as Passover, Rosh Hashanah, and Hanukkah, offer opportunities for celebration, reflection, and community.
- Life-Cycle Events: From naming ceremonies to funerals, Jewish life-cycle events are rich in tradition and meaning, offering support and guidance through life's journeys.
The Jewish Community: A Global Family United by Faith
The Jewish community, spanning across the globe, is a diverse and vibrant entity, united by shared faith and cultural heritage. Despite geographical distances, Jewish communities maintain strong connections, fostering a sense of global unity.
Jewish communities are characterized by their commitment to education, with a focus on Jewish studies and cultural preservation. Synagogues, community centers, and schools serve as hubs for religious practice, social interaction, and cultural expression.
Jewish Education and Cultural Preservation
Jewish education is a cornerstone of community life, ensuring the transmission of Jewish values, traditions, and knowledge to future generations. From early childhood education to adult learning programs, Jewish communities invest significantly in educational initiatives.
Cultural preservation is another key aspect of Jewish community life. From language classes to culinary events, Jewish communities celebrate their rich cultural heritage, ensuring its continued vitality and relevance.
| Community Initiative | Impact |
|---|---|
| Jewish Schools | Provide a comprehensive education, combining academic excellence with Jewish studies, ensuring the next generation is well-equipped to contribute to both Jewish and broader society. |
| Community Events | Foster a sense of community, bringing people together for social, cultural, and religious events, strengthening bonds and promoting a sense of belonging. |
Judaism's Impact on the World: A Faith with Global Reach
Judaism's influence extends far beyond its religious and cultural boundaries, shaping the broader global landscape in significant ways. From its contributions to philosophy and ethics to its impact on modern society, Judaism has left an indelible mark on the world.
Philosophical and Ethical Contributions
Jewish thinkers and philosophers have made significant contributions to the fields of philosophy and ethics. From the ancient world to modern times, Jewish scholars have engaged in deep intellectual discourse, exploring questions of existence, morality, and the nature of God. These contributions have shaped Western thought, influencing philosophical traditions and ethical frameworks.
Jewish ethics, grounded in the Torah and rabbinic teachings, emphasize the importance of compassion, justice, and moral responsibility. Concepts like tikkun olam (repairing the world) and tzedakah (charity and justice) have influenced social and ethical movements, inspiring action towards a more just and compassionate world.
Social and Cultural Influence
Judaism has had a profound impact on social and cultural movements, shaping ideas and values that have resonated globally. From the fight for civil rights to the promotion of social justice, Jewish values and traditions have inspired and guided social change.
Jewish culture, rich in tradition and creativity, has also made significant contributions to the arts, literature, and music. Jewish artists, writers, and musicians have left an indelible mark on the cultural landscape, enriching the global artistic canon.
The Future of Judaism: Embracing Change and Continuity
As Judaism continues to evolve in a rapidly changing world, it faces both challenges and opportunities. The Jewish community is navigating a delicate balance between preserving traditional values and embracing modern innovations.
The digital age has brought new opportunities for Jewish engagement, with online platforms and virtual communities offering new avenues for connection and learning. At the same time, the Jewish community is addressing complex issues, from interfaith dialogue to the role of women in religious leadership, shaping the future of Judaism.
Navigating Modern Challenges
Modern challenges, such as antisemitism and religious intolerance, continue to impact the Jewish community. Jewish leaders and organizations are working tirelessly to address these issues, promoting understanding and tolerance through education and advocacy.
The Jewish community is also grappling with issues of identity and inclusion, striving to create a more welcoming and diverse environment. Efforts to promote equality and inclusion are shaping the future of Jewish life, ensuring that Judaism remains a vibrant and relevant faith for all.
FAQs
What are the key beliefs of Judaism?
+Judaism's core beliefs include monotheism, the belief in one God, and the importance of living a righteous and ethical life guided by the Torah and rabbinic teachings. Key principles include the concept of mitzvot (commandments) and the emphasis on compassion, justice, and moral responsibility.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How does Judaism influence modern society?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Judaism has had a profound impact on modern society, shaping philosophical and ethical discourse. Jewish values and traditions have influenced social movements, inspiring action towards justice and compassion. Jewish culture has also enriched the global artistic landscape, leaving a lasting legacy.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are some key Jewish festivals and their significance?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Jewish festivals, such as Passover, Rosh Hashanah, and Hanukkah, are significant for various reasons. Passover celebrates the liberation of the Israelites from slavery in Egypt. Rosh Hashanah marks the Jewish New Year and is a time for reflection and renewal. Hanukkah commemorates the rededication of the Second Temple in Jerusalem.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How does the Jewish community promote education and cultural preservation?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The Jewish community promotes education through a range of initiatives, including Jewish schools and adult learning programs. Cultural preservation is also a key focus, with language classes, culinary events, and community gatherings celebrating Jewish heritage and traditions.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are some challenges facing the Jewish community today?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The Jewish community faces challenges such as antisemitism, religious intolerance, and issues of identity and inclusion. Jewish leaders and organizations are actively addressing these challenges through education, advocacy, and efforts to create a more welcoming and diverse community.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>