Function Of Parts Of The Brain
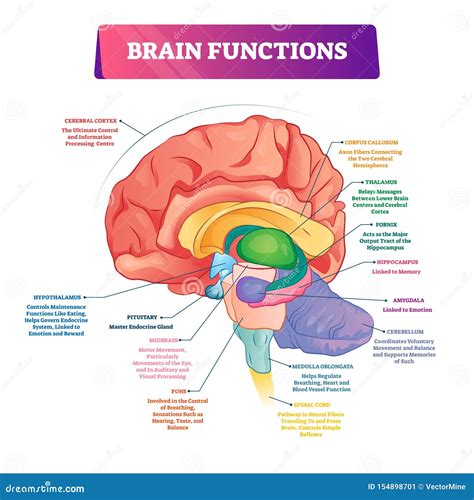
The human brain is a fascinating and complex organ, often referred to as the command center of the body. It is responsible for an array of functions that enable us to think, feel, move, and experience the world around us. Each part of the brain has a specific role, contributing to our overall cognitive and physical abilities. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate functions of the different parts of the brain, exploring their unique contributions to our daily lives.
Cerebrum: The Center of Higher Cognitive Functions

The cerebrum, often considered the most distinctive feature of the human brain, is a highly developed structure that occupies a significant portion of the cranial cavity. It is divided into two hemispheres: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere, each responsible for different aspects of our cognitive processes.
Left Hemisphere: Language and Logical Thinking
The left hemisphere of the cerebrum is often associated with language and logical thought processes. It is crucial for understanding and producing speech, as well as for tasks that require analytical thinking, such as solving mathematical problems or following logical sequences.
Within the left hemisphere, the Broca’s area is responsible for speech production, enabling us to articulate our thoughts and express ourselves verbally. On the other hand, the Wernicke’s area plays a vital role in language comprehension, allowing us to understand the spoken and written word.
Furthermore, the left hemisphere is involved in tasks that require precision and detail, such as reading, writing, and solving complex mathematical equations. It is also responsible for controlling the muscles on the right side of the body, demonstrating its crucial role in our physical abilities.
Right Hemisphere: Creative and Visual Thinking
In contrast, the right hemisphere of the cerebrum is associated with creative and visual thinking. It excels in tasks that require spatial awareness, such as recognizing faces, interpreting non-verbal cues, and understanding visual concepts.
The right hemisphere is also responsible for emotional processing and creative endeavors. It plays a crucial role in our ability to express and recognize emotions, as well as in activities that require artistic or musical skills. Additionally, it controls the muscles on the left side of the body, ensuring coordinated movement.
Both hemispheres of the cerebrum are interconnected through the corpus callosum, a bundle of nerve fibers that enables communication and coordination between the two sides. This allows for the integration of information and the execution of complex tasks that require both logical and creative thinking.
Cerebellum: The Coordinator of Movement

Located at the back of the brain, the cerebellum is a relatively small structure that plays a critical role in coordinating movement and maintaining balance. It receives input from the sensory systems, the spinal cord, and other parts of the brain, and integrates this information to produce smooth and precise movements.
Role in Motor Control
The cerebellum is essential for fine-tuning motor skills and ensuring that our movements are accurate and well-timed. It receives signals from the cerebrum regarding intended movements and then adjusts these signals based on sensory feedback, such as visual input or proprioception (the sense of body position and movement).
For example, when you reach for a cup of coffee, the cerebellum helps to adjust the trajectory of your hand to ensure it lands precisely on the cup. It also plays a crucial role in maintaining balance, especially when we are in motion, such as walking or running.
Involvement in Learning and Memory
Surprisingly, the cerebellum is not only involved in motor control but also in learning and memory processes. It contributes to procedural memory, which is responsible for skills and habits that become automatic with practice, such as riding a bike or typing.
The cerebellum’s role in learning is evident in its ability to adapt and refine motor skills based on experience. It helps us to improve our performance over time, whether it’s learning a new sport or mastering a musical instrument.
Brain Stem: The Vital Link to Survival
The brain stem, situated beneath the cerebrum and in front of the cerebellum, serves as a vital link between the brain and the spinal cord. It is responsible for maintaining basic life functions and controlling many of our automatic and instinctual behaviors.
Regulating Vital Functions
The brain stem plays a crucial role in regulating vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure. It receives input from various body systems and adjusts these vital functions accordingly to ensure our survival.
For instance, when we experience a stressful situation, the brain stem activates the sympathetic nervous system, which triggers the “fight-or-flight” response. This response prepares our body for action by increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and redirecting blood flow to essential organs and muscles.
Involvement in Sleep and Arousal
The brain stem also plays a significant role in regulating our sleep-wake cycle and controlling arousal levels. It contains structures such as the reticular activating system, which is responsible for maintaining consciousness and wakefulness.
During sleep, the brain stem helps to regulate the different stages of sleep, ensuring we progress through the sleep cycle and experience restorative rest. It also plays a role in awakening, as it receives input from the environment and helps to rouse us from sleep when necessary.
Limbic System: The Emotional Hub
The limbic system is a group of interconnected structures located deep within the brain that plays a crucial role in our emotional responses, memory formation, and motivation. It is often referred to as the “emotional hub” of the brain due to its significant influence on our feelings and behaviors.
Amygdala: Emotional Processing
The amygdala, a small, almond-shaped structure within the limbic system, is heavily involved in emotional processing. It plays a key role in detecting and responding to threats, triggering the fear response and activating the fight-or-flight reaction.
The amygdala is also responsible for attaching emotional significance to memories, helping us to remember events that are emotionally charged. This is why emotional memories often feel more vivid and easily recalled than neutral memories.
Hippocampus: Memory Formation
The hippocampus, another crucial structure in the limbic system, is primarily responsible for the formation of new memories, particularly those related to spatial navigation and contextual information.
It plays a vital role in converting short-term memories into long-term memories, a process known as memory consolidation. The hippocampus is particularly important for episodic memory, which involves recalling specific events and experiences.
Thalamus: Sensory Relay Station
The thalamus, a small structure located near the center of the brain, acts as a sensory relay station, receiving and processing sensory information from various parts of the body and sending it to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex for further analysis.
It plays a crucial role in regulating our awareness of the surrounding environment, as well as in maintaining consciousness and alertness. The thalamus is also involved in the regulation of sleep and wakefulness, ensuring a balanced and restorative sleep-wake cycle.
The Fascinating World of Brain Function

The human brain is an incredibly complex organ, with each part playing a unique and essential role in our daily lives. From the cerebrum’s higher cognitive functions to the cerebellum’s coordination of movement, the brain stem’s regulation of vital functions, and the limbic system’s emotional responses, every aspect contributes to our ability to think, feel, and interact with the world around us.
Understanding the functions of different parts of the brain not only sheds light on the intricate workings of our bodies but also highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy brain throughout our lives. By appreciating the complexity and uniqueness of our brains, we can strive to nurture and support their optimal functioning, ensuring a healthy and fulfilling life.
| Brain Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Cerebrum | Higher cognitive functions, language, logical thinking, and creative thinking |
| Cerebellum | Coordination of movement, balance, and learning |
| Brain Stem | Regulation of vital functions, sleep-wake cycle, and arousal |
| Limbic System | Emotional processing, memory formation, and motivation |

How does the brain’s structure influence our behavior and personality?
+The brain’s structure and organization play a significant role in shaping our behavior and personality. Different regions of the brain are responsible for various cognitive functions, emotions, and behaviors. For instance, the prefrontal cortex is associated with decision-making, impulse control, and personality traits. Damage or abnormalities in specific brain regions can lead to changes in behavior, mood, or cognitive abilities.
Can brain function be improved through lifestyle choices?
+Absolutely! Engaging in regular physical exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, getting sufficient sleep, and participating in mentally stimulating activities can all positively impact brain function. These lifestyle choices promote brain health, enhance cognitive abilities, and may even slow down age-related cognitive decline.
What are some common disorders or conditions associated with specific brain regions?
+Various disorders and conditions are linked to specific brain regions. For example, Alzheimer’s disease is associated with degeneration in the hippocampus and other parts of the temporal lobe, impacting memory and cognitive functions. Parkinson’s disease is linked to the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, affecting movement and coordination. These are just a few examples, and each brain region can be associated with a range of disorders and conditions.


