Feeling Bruised All Over Body
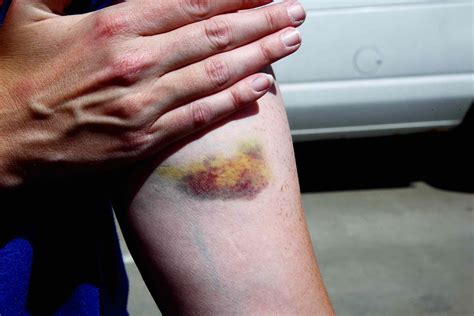
Have you ever experienced those mysterious bruises that seem to appear out of nowhere, leaving you wondering what caused them and if something might be amiss with your health? Bruising, medically known as contusion, is a common occurrence that can affect people of all ages. While minor bruises are typically harmless and often result from everyday activities or accidents, excessive bruising can sometimes be a sign of an underlying health condition. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and when to seek medical attention is crucial for maintaining your well-being.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various factors that contribute to bruising, explore the different types of bruises, and provide valuable insights into when you should consult a healthcare professional. By the end of this article, you'll have a clearer understanding of bruising, its potential implications, and the steps you can take to address any concerns.
Understanding Bruising: Causes and Risk Factors
Bruises are a visible sign of damage to the small blood vessels beneath the skin. When these blood vessels break, blood leaks into the surrounding tissue, causing the characteristic discoloration we associate with bruises. While some bruising is normal and expected, certain factors can increase your susceptibility to bruising or indicate an underlying issue.
Common Causes of Bruising
The most frequent cause of bruises is accidental injury or trauma. Everyday activities like bumping into furniture, engaging in sports, or even roughhousing with pets can lead to minor bruises. Additionally, as we age, our skin becomes thinner and more delicate, making it easier to develop bruises. This is particularly true for individuals over the age of 50, as the skin's natural protective layer weakens over time.
Certain medications can also increase your risk of bruising. Blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or warfarin, are commonly prescribed to prevent blood clots but can make bruising more likely. Additionally, some herbal supplements and vitamins, like ginkgo biloba and vitamin E, have blood-thinning properties and may contribute to easier bruising.
Underlying Health Conditions
While most bruises are benign, excessive or frequent bruising can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying health issue. Here are some medical conditions associated with increased bruising:
- Vitamin Deficiencies: A lack of vitamin C or vitamin K in your diet can affect your body's ability to produce collagen and blood clotting factors, leading to easier bruising.
- Blood Disorders: Certain blood disorders, such as hemophilia or thrombocytopenia, can cause excessive bruising. These conditions affect the blood's ability to clot properly, resulting in prolonged bleeding and increased bruising.
- Liver Disease: The liver plays a crucial role in blood clotting. Liver disease or liver failure can disrupt this process, leading to abnormal bleeding and bruising.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the blood vessels and platelets, making them more susceptible to damage and increasing the risk of bruising.
- Cancer: Certain types of cancer, such as leukemia or multiple myeloma, can affect the blood and bone marrow, leading to decreased platelet counts and increased bruising.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
In addition to medical conditions, several lifestyle and environmental factors can influence bruising. These include:
- Sun Exposure: Excessive sun exposure can damage the skin and make it more susceptible to bruising. Always wear sunscreen and protective clothing when outdoors to minimize this risk.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can thin the blood and increase bruising. Moderate your alcohol consumption to reduce this effect.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A diet lacking in essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C and vitamin K, can weaken the skin and blood vessels, making bruising more likely.
- Environmental Hazards: Working in hazardous environments or engaging in activities with a high risk of injury can increase your chances of developing bruises.
Types of Bruises and Their Characteristics

Bruises can vary in appearance, size, and location on the body. Understanding the different types of bruises can help you identify potential causes and determine when to seek medical attention.
Superficial Bruises
Superficial bruises, also known as ecchymoses, are the most common type and typically occur on the skin's surface. They are often the result of minor injuries or bumps and are characterized by a localized area of discoloration. Superficial bruises can range in color from blue, purple, or black to green or yellow as they heal. They usually resolve on their own within a few weeks.
Deep Bruises
Deep bruises, or hematomas, occur when blood collects in a specific area beneath the skin. These bruises are often the result of more severe injuries or accidents and can be quite painful. They are typically larger in size and may take longer to heal. Deep bruises can also be accompanied by swelling and tenderness in the affected area.
Petechiae and Purpura
Petechiae and purpura are smaller forms of bruises that appear as tiny red or purple spots on the skin. Petechiae are typically less than 3 millimeters in diameter and are caused by broken capillaries. Purpura, on the other hand, are larger and can be up to 1 centimeter in diameter. Both petechiae and purpura can indicate an underlying medical condition and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Black Eye
A black eye, or periorbital hematoma, is a type of bruise that occurs around the eye. It is often the result of a blow to the face or head and is characterized by swelling and discoloration around the eye socket. Black eyes can be quite painful and may take several weeks to fully heal.
| Bruise Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Superficial Bruises | Localized discoloration, heals within a few weeks |
| Deep Bruises | Larger, painful, accompanied by swelling |
| Petechiae | Tiny red or purple spots, caused by broken capillaries |
| Purpura | Larger spots, may indicate an underlying condition |
| Black Eye | Swelling and discoloration around the eye, painful and slow to heal |
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most bruises are harmless and resolve on their own, there are certain situations where seeking medical attention is crucial. Here are some signs and symptoms that indicate you should consult a healthcare professional:
- Excessive or Frequent Bruising: If you notice an increase in the number of bruises you develop, especially if you're not engaging in activities that typically cause bruising, it's important to see a doctor. Frequent or unexplained bruising can be a sign of an underlying health issue.
- Painful or Large Bruises: Deep bruises or those accompanied by severe pain and swelling should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. These types of bruises may require medical treatment to prevent further complications.
- Bruising in Unusual Places: Bruises on the torso, back, or areas not typically associated with everyday activities may indicate an underlying condition. Consult a doctor if you notice bruises in unusual locations.
- Bruising with Other Symptoms: If you experience bruising along with other symptoms like fatigue, unexplained weight loss, frequent infections, or easy bleeding, it's essential to seek medical advice. These symptoms may be indicative of a more serious condition.
- Bruising after Minor Injuries: If you develop bruises after seemingly minor injuries or accidents, it could be a sign of an underlying bleeding disorder. Consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Medical Tests and Diagnosis
If your doctor suspects an underlying condition based on your bruising and other symptoms, they may recommend various tests to determine the cause. These tests may include:
- Blood Tests: A complete blood count (CBC) can assess your red and white blood cell counts, as well as platelet levels. Other blood tests may be ordered to check for specific conditions, such as liver function or vitamin deficiencies.
- Imaging Tests: Depending on your symptoms and medical history, your doctor may recommend imaging tests like an X-ray, CT scan, or MRI to evaluate the extent of bruising or rule out other conditions.
- Bone Marrow Aspiration and Biopsy: In cases where a blood disorder is suspected, a bone marrow aspiration and biopsy may be performed to examine the bone marrow and determine if there are any abnormalities.
Treatment and Management of Bruising
The treatment and management of bruising depend on the underlying cause. For minor bruises resulting from everyday activities, home care measures are typically sufficient. These include:
- Rest and Ice: Apply ice or a cold pack to the bruised area for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce swelling and pain.
- Elevation: Elevate the bruised area above the level of your heart to help reduce swelling and promote healing.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage or wrap to provide support and reduce swelling.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with bruises.
- Time: Most minor bruises will heal on their own within a few weeks. Patience and proper care are key during the healing process.
For more severe or persistent bruising, or if an underlying medical condition is identified, your doctor may recommend specific treatments. These can include:
- Medications: Depending on the underlying condition, your doctor may prescribe medications to address the root cause of excessive bruising. This could include blood-thinning medications, vitamin supplements, or medications to treat autoimmune disorders.
- Physical Therapy: In cases where bruising is related to muscle or bone injuries, physical therapy can help improve strength, flexibility, and mobility.
- Surgery: For certain conditions, such as liver disease or severe blood disorders, surgery may be necessary to treat the underlying issue and prevent further complications.
Preventing Bruises
While it's not always possible to prevent bruises entirely, especially those resulting from accidental injuries, there are some measures you can take to reduce your risk:
- Protect Your Skin: Wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves and pants, when engaging in activities that may pose a risk of injury. Use sunscreen and protective gear when spending time outdoors to minimize sun-related skin damage.
- Avoid Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Limit your alcohol intake to reduce the thinning of your blood and the risk of bruising.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Ensure your diet is rich in essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C and vitamin K, to support healthy skin and blood vessel function.
- Exercise Caution: Be mindful of your surroundings and take precautions to avoid accidents and injuries. Wear appropriate safety gear when engaging in sports or hazardous activities.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: If you have an underlying medical condition that increases your risk of bruising, work closely with your healthcare team to manage and treat the condition effectively.
Conclusion
Bruising is a common occurrence that can have various causes, ranging from everyday accidents to underlying medical conditions. While most bruises are harmless and resolve on their own, excessive or unexplained bruising should not be ignored. Understanding the different types of bruises, their potential causes, and when to seek medical attention is essential for maintaining your overall health and well-being.
By staying informed and taking proactive measures to prevent and manage bruising, you can ensure that any concerns are addressed promptly and effectively. Remember, your health is a priority, and seeking professional guidance when needed is always a wise decision.
Can stress cause bruising?
+While stress itself does not directly cause bruising, it can impact your overall health and immune system. Chronic stress can weaken your body’s ability to fight off infections and maintain healthy blood circulation, potentially increasing your susceptibility to bruising. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and a healthy lifestyle can help improve your overall well-being and reduce the risk of bruising.
Are there any home remedies to speed up bruise healing?
+While there are no magical home remedies to instantly heal bruises, some natural remedies can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Applying arnica gel or cream to the bruised area can provide some relief and potentially speed up the healing process. Additionally, consuming foods rich in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits and leafy greens, can support collagen production and aid in bruise healing.
How long does it typically take for bruises to heal?
+The healing time for bruises can vary depending on the severity and location of the bruise. Superficial bruises on the skin’s surface typically heal within a few weeks. Deeper bruises or those affecting the muscles may take longer, sometimes up to several months. Patience and proper care during the healing process are essential.