What's Healthy Bmi
Understanding Body Mass Index (BMI) is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and assessing overall well-being. While it's not a perfect measure, BMI provides a simple and widely used tool to categorize individuals based on their height and weight. In this article, we will delve into the concept of a healthy BMI, explore its calculation, and discuss its implications for individuals of all ages.
Unraveling the Concept of Healthy BMI

Body Mass Index, or BMI, is a numerical value that helps determine whether an individual’s weight is within a healthy range. It is calculated by dividing an individual’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. The resulting value is then categorized into various ranges, each indicating a different level of weight status.
The concept of a healthy BMI is rooted in the idea that a specific weight range is optimal for an individual's overall health. While BMI is a useful tool, it is important to note that it is just one aspect of a comprehensive health assessment. Other factors such as body composition, muscle mass, and overall fitness levels also play significant roles in determining an individual's overall well-being.
The BMI Categories
The World Health Organization (WHO) has established standard BMI categories, which are widely recognized and used by healthcare professionals worldwide. These categories are as follows:
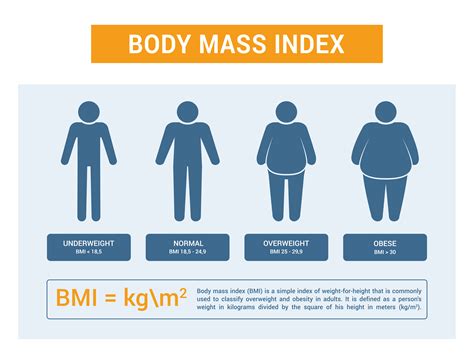
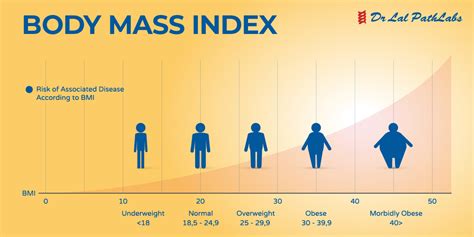
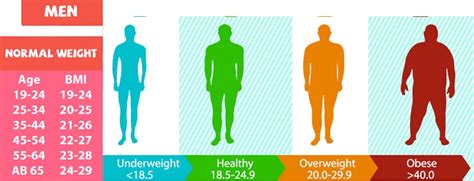
- Underweight: BMI below 18.5
- Normal Weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obese: BMI of 30 or above
These categories provide a general framework for understanding weight status, but it's important to remember that BMI is just one indicator and should not be the sole determinant of health.
The Impact of BMI on Health
A healthy BMI is associated with a reduced risk of various health conditions. Individuals within the normal weight range are generally at a lower risk for diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and joint problems. Maintaining a healthy BMI can contribute to improved overall health and well-being.
However, it's crucial to consider that BMI may not accurately reflect the health status of individuals with high muscle mass or certain medical conditions. For instance, athletes or individuals with a high muscle-to-fat ratio may have a higher BMI but still be considered healthy. Similarly, older adults or those with certain medical conditions may have a lower BMI but still require attention to their nutritional needs and overall health.
| BMI Category | Health Implications |
|---|---|
| Underweight | Risk of nutritional deficiencies, weakened immune system, and increased vulnerability to illness. |
| Normal Weight | Optimal weight range, reduced risk of chronic diseases, and improved overall health. |
| Overweight | Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and joint problems. |
| Obese | High risk of severe health conditions, including heart disease, stroke, and certain cancers. |
Calculating Your BMI
Calculating your BMI is a straightforward process. You can use the following formula:
BMI = Weight (kg) / (Height (m))2
For those who prefer using pounds and inches, here's an alternative formula:
BMI = Weight (lbs) / (Height (in))2 x 703
You can also use online BMI calculators or mobile apps to determine your BMI. These tools provide a quick and convenient way to assess your weight status.
Interpreting Your BMI
Once you have calculated your BMI, it’s important to understand what the resulting value means. As mentioned earlier, the WHO’s BMI categories are a useful guide:
- Under 18.5: This indicates that you are underweight and may need to gain weight to improve your health.
- 18.5 to 24.9: A BMI within this range is considered normal and healthy. It suggests that you are at a lower risk for weight-related health issues.
- 25 to 29.9: Being in the overweight category means you may benefit from weight loss to reduce your risk of certain health conditions.
- 30 or above: Obesity is a serious health concern, and individuals with a BMI of 30 or higher may require medical intervention and lifestyle changes to improve their health.
Maintaining a Healthy BMI
Achieving and maintaining a healthy BMI involves a balanced approach to nutrition and physical activity. Here are some key strategies:
- Nutrition: Focus on a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods. Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Avoid excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and high-calorie snacks.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week. Incorporate strength training and flexibility exercises for overall fitness.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes. Avoid overeating and listen to your body's hunger cues. Use smaller plates and take time to savor your meals.
- Healthy Habits: Adopt healthy lifestyle choices such as adequate sleep, stress management, and hydration. These factors contribute to overall well-being and can impact weight management.
BMI and Individual Variations
It’s important to remember that BMI is a general tool and may not accurately reflect the health status of every individual. Factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, and body composition can influence the interpretation of BMI.
For instance, older adults may have a lower BMI due to age-related muscle loss, but this doesn't necessarily indicate poor health. Similarly, certain ethnic groups may have different BMI thresholds for health risks. It's crucial to consult with healthcare professionals who can provide personalized guidance based on your unique circumstances.
BMI for Different Age Groups
BMI interpretations can vary based on age. Here’s a breakdown of BMI considerations for different age groups:
Children and Adolescents
For children and adolescents, BMI is calculated similarly to adults, but the interpretation differs. Growth charts and percentile curves are used to compare an individual’s BMI with others of the same age and gender. This allows healthcare professionals to assess their growth and development.
A healthy BMI for children and adolescents typically falls within the 5th to 85th percentile range. Those below the 5th percentile may be considered underweight, while those above the 85th percentile may be at risk for overweight or obesity.
Adults
For adults, the standard BMI categories mentioned earlier apply. However, it’s important to note that muscle mass and body composition can significantly impact BMI. As mentioned earlier, individuals with high muscle mass may have a higher BMI but still be considered healthy.
Older Adults
In older adults, BMI interpretations can be more complex. As mentioned earlier, age-related muscle loss can lead to a lower BMI, but this doesn’t always indicate poor health. Healthcare professionals often consider additional factors such as body composition, functional ability, and overall health status when assessing the health of older adults.
The Limitations of BMI
While BMI is a widely used tool, it has its limitations. Here are some key considerations:
- Does Not Account for Body Composition: BMI does not differentiate between muscle and fat. As a result, individuals with high muscle mass may have a higher BMI but still be considered healthy.
- May Not Apply to Certain Populations: BMI interpretations may not be accurate for certain populations, such as pregnant women, highly muscular individuals, or those with certain medical conditions.
- Does Not Reflect Health Status: BMI is just one indicator and should not be the sole determinant of health. Other factors such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and overall fitness also play crucial roles.
Conclusion: Striving for a Healthy BMI
Understanding and maintaining a healthy BMI is an important aspect of overall well-being. While BMI provides a useful framework for weight categorization, it’s essential to recognize its limitations and consider other health indicators. Achieving and sustaining a healthy BMI involves adopting a balanced lifestyle, including nutritious eating habits and regular physical activity.
By staying informed and consulting with healthcare professionals, individuals can make informed decisions about their weight and overall health. Remember, a healthy BMI is just one piece of the puzzle, and a holistic approach to wellness is key to leading a healthy and fulfilling life.
How accurate is BMI as a measure of health?
+BMI is a useful tool, but it has limitations. It does not account for body composition and may not accurately reflect the health status of individuals with high muscle mass or certain medical conditions. Other health assessments, such as blood pressure and cholesterol levels, are also important.
What if my BMI falls outside the normal range?
+If your BMI falls outside the normal range, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized guidance and help you understand the implications for your health. Making positive lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet and increasing physical activity, can be beneficial.
Can BMI change with age?
+Yes, BMI can change with age. As individuals age, they may experience muscle loss and changes in body composition, which can affect their BMI. It’s important to consider age-related factors when interpreting BMI, especially in older adults.



