What Organs Are In The Muscular System
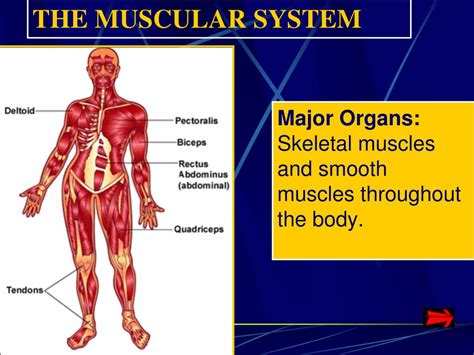
The muscular system is an intricate network of tissues and organs that play a vital role in the human body, facilitating movement, maintaining posture, and generating heat. While muscles are the primary actors in this system, it is essential to understand the other organs that contribute to its overall function and coordination.
The Primary Organs of the Muscular System

The muscular system is composed of a wide range of specialized tissues, each with unique characteristics and functions. Here, we delve into the key organs that form the foundation of this system.
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles are the most visible and arguably the most recognizable organs of the muscular system. Attached to the bones of the skeleton, these muscles are responsible for voluntary movements. They are characterized by their striated appearance and their ability to contract and relax, allowing for a wide range of motions. Skeletal muscles are under the control of the somatic nervous system, which enables conscious control over their movements.
| Skeletal Muscle | Function |
|---|---|
| Biceps Brachii | Flexion of the elbow and rotation of the forearm |
| Quadriceps Femoris | Extension of the knee and stabilization of the patella |
| Deltoid | Abduction, flexion, and extension of the arm |

Smooth Muscles
Unlike skeletal muscles, smooth muscles are involuntary and are found within the walls of various organs and structures in the body. They are characterized by their non-striated appearance and their ability to contract rhythmically. Smooth muscles are controlled by the autonomic nervous system, which regulates their activity without conscious control. These muscles play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and facilitating involuntary movements.
| Smooth Muscle | Function |
|---|---|
| Digestive Smooth Muscle | Peristalsis in the gastrointestinal tract |
| Uterine Smooth Muscle | Contraction during childbirth |
| Blood Vessel Smooth Muscle | Vasoconstriction and vasodilation to regulate blood flow |
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle is a specialized type of muscle found exclusively in the heart. It is responsible for the rhythmic contractions that pump blood throughout the body. Like smooth muscles, cardiac muscles are involuntary and are controlled by the autonomic nervous system. However, they have unique characteristics that distinguish them from other muscle types, including their branching appearance and their ability to self-regulate their contractions.
Other Organs Involved in the Muscular System

While muscles are the primary organs of the muscular system, several other organs play a crucial role in its overall function and coordination.
The Nervous System
The nervous system is an integral part of the muscular system, responsible for sending electrical signals that trigger muscle contractions. It consists of the brain, spinal cord, and a vast network of nerves that connect to muscles throughout the body. The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements, while the autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary muscle activity.
The Endocrine System
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating muscle function and performance. Hormones secreted by various glands, such as testosterone and growth hormone, influence muscle growth, repair, and strength. The endocrine system also interacts with the nervous system to coordinate muscle activity and maintain homeostasis.
Connective Tissues
Connective tissues, such as tendons and ligaments, provide crucial support and attachment for muscles. Tendons connect muscles to bones, allowing for the transmission of force during movement. Ligaments, on the other hand, connect bones to other bones, providing stability and support for joints. These connective tissues are essential for the proper functioning of the muscular system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary function of the muscular system?
+The primary function of the muscular system is to facilitate movement, maintain posture, and generate heat. It works in coordination with other body systems to ensure the body’s overall health and functionality.
How do skeletal muscles differ from smooth and cardiac muscles?
+Skeletal muscles are voluntary and striated, attached to bones for movement. Smooth muscles are involuntary, non-striated, and found in organs like the digestive tract. Cardiac muscles are also involuntary, with unique branching characteristics, and are found only in the heart.
What role do hormones play in the muscular system?
+Hormones, produced by the endocrine system, regulate muscle growth, repair, and strength. Testosterone and growth hormone, for example, play a crucial role in muscle development and maintenance.



