What Are The Functions Of Neurons
The human brain, an incredibly complex organ, is composed of billions of neurons, each serving vital functions that enable our thoughts, actions, and perceptions. Understanding the role of neurons is fundamental to grasping the intricacies of the nervous system and its impact on our daily lives. This article delves into the fascinating world of neurons, shedding light on their structure, types, and the crucial functions they perform.
The Structure and Types of Neurons
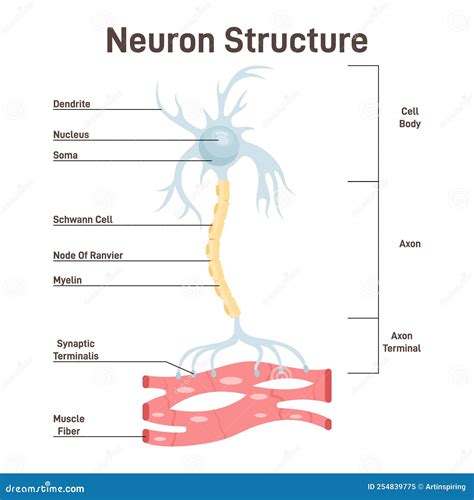
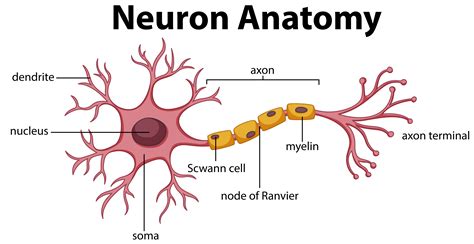
Neurons, also known as nerve cells, are specialized cells that transmit information throughout the body. They are the building blocks of the nervous system, forming a complex network that facilitates communication and coordination. The structure of a neuron consists of three main parts: the cell body, dendrites, and an axon.
The cell body (soma) is the central part of the neuron, containing the nucleus and other essential cellular components. It provides the necessary metabolic support for the neuron to function. Extending from the cell body are numerous dendrites, which are branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons. These signals are then processed and integrated in the cell body.
The axon is another critical component of a neuron. It is a long, slender projection that transmits electrical signals known as action potentials away from the cell body. At the end of the axon, there are specialized structures called axon terminals, which release chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters enable communication between neurons by crossing the gap, known as the synaptic cleft, to bind with receptors on the dendrites of neighboring neurons.
Neurons come in various types, each designed for specific functions. The three primary types are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons.
- Sensory Neurons: These neurons receive and transmit sensory information from various parts of the body to the central nervous system. They play a crucial role in our perception of the external world, allowing us to feel, see, hear, taste, and smell.
- Motor Neurons: Motor neurons are responsible for sending signals from the central nervous system to muscles and glands. They enable us to perform voluntary actions, such as walking, talking, and grasping objects, as well as involuntary actions like breathing and digestion.
- Interneurons: Interneurons, also known as association neurons, connect neurons within the central nervous system. They form intricate networks, facilitating communication and coordination between different parts of the brain and spinal cord. Interneurons play a vital role in processing and integrating information, shaping our thoughts, memories, and responses to stimuli.
The Functions of Neurons
Neurons perform a multitude of functions, each contributing to the overall functioning of the nervous system and, consequently, our behavior and experiences.
Information Transmission
One of the primary functions of neurons is to transmit information rapidly and accurately. This information can be sensory data, such as the touch of a feather or the sound of a bird’s song, or it can be commands from the brain to initiate movement. Neurons achieve this transmission through a series of electrical and chemical signals, ensuring that information reaches its destination efficiently.
Processing and Integration
Neurons don’t merely transmit data; they also process and integrate it. When a neuron receives multiple signals from different sources, it integrates these inputs to generate an output. This output can be a simple relay of information to other neurons or a more complex response, depending on the type of neuron and its function.
Generating Responses
Neurons are integral to generating responses to internal and external stimuli. Whether it’s the decision to reach for a cup of coffee or the reflexive withdrawal from a hot surface, neurons play a critical role. They receive sensory input, process it, and send commands to the appropriate muscles or glands, resulting in a response.
Learning and Memory
The ability to learn and remember is closely tied to the functioning of neurons. When we learn something new, neurons form new connections or strengthen existing ones. This process, known as synaptic plasticity, is the basis for memory formation. Different regions of the brain, such as the hippocampus and the cerebral cortex, are involved in different types of memory, and neurons within these regions play specific roles in encoding, storing, and retrieving memories.
Regulating Homeostasis
Neurons also contribute to maintaining homeostasis, the body’s internal balance. They regulate various physiological processes, including body temperature, blood pressure, and hormone levels. For instance, neurons in the hypothalamus help maintain body temperature by triggering shivering or sweating in response to changes in external temperature.
| Neuron Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Sensory Neurons | Transmit sensory information from the body to the central nervous system. |
| Motor Neurons | Send commands from the central nervous system to muscles and glands, enabling movement and involuntary actions. |
| Interneurons | Facilitate communication and coordination within the central nervous system, processing and integrating information. |
Conclusion
Neurons, with their intricate structure and diverse functions, are the cornerstone of the nervous system. From transmitting information to regulating our internal environment, they play a vital role in our daily lives. Understanding the functions of neurons not only provides insight into the workings of the brain but also highlights the incredible complexity and sophistication of the human body.
How do neurons communicate with each other?
+
Neurons communicate through a process called synaptic transmission. This involves the release of neurotransmitters from the axon terminal of one neuron, which then diffuse across the synaptic cleft to bind with receptors on the dendrites of the neighboring neuron. This triggers an electrical response in the receiving neuron, which can either excite or inhibit it, depending on the type of neurotransmitter and receptor involved.
What is the role of glial cells in relation to neurons?
+
Glial cells, often referred to as the “support cells” of the nervous system, play a crucial role in supporting and protecting neurons. They provide physical support, help maintain the blood-brain barrier, and contribute to the formation of the myelin sheath, which insulates axons and speeds up the transmission of electrical signals. Additionally, glial cells are involved in nutrient supply, waste removal, and immune responses within the nervous system.
Can neurons regenerate or repair themselves if damaged?
+
In general, neurons in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) have limited regenerative capacity. Unlike many other cells in the body, neurons do not typically divide and replace themselves when damaged. However, there are some exceptions, such as certain types of neurons in the hippocampus and the olfactory bulb, which can regenerate under specific conditions. In the peripheral nervous system, some types of neurons can regenerate if they are partially damaged.
How do neurons contribute to diseases and disorders of the nervous system?
+
Neurons are central to many neurological and psychiatric disorders. Conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis involve the dysfunction or loss of specific types of neurons. For example, in Parkinson’s disease, neurons in a specific region of the brain that produce dopamine degenerate, leading to movement disorders. Similarly, in psychiatric disorders like depression and schizophrenia, imbalances in neurotransmitters and alterations in neural circuits involving various types of neurons are implicated.
What are some advancements in neuroscience research that are improving our understanding of neurons?
+
Advancements in neuroscience research are continuously enhancing our understanding of neurons and the nervous system. Techniques like optogenetics, which allows scientists to control neurons with light, have revolutionized our ability to study neural circuits. Additionally, advancements in imaging technologies, such as functional MRI (fMRI) and two-photon microscopy, enable researchers to visualize neural activity in real time. These and other cutting-edge tools are providing unprecedented insights into the structure, function, and connectivity of neurons, paving the way for improved treatments for neurological disorders.

