Vitamin B12 Is Good For

Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a vital nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It is an essential component for various bodily functions and is often touted for its numerous benefits. This article aims to delve into the world of Vitamin B12, exploring its significance, sources, and the positive impacts it can have on our bodies. From cognitive function to energy production, we will uncover the reasons why Vitamin B12 is considered a powerhouse nutrient.
Understanding Vitamin B12 and Its Importance

Vitamin B12, a water-soluble vitamin, is unique in its chemical structure and function. Unlike other B vitamins, it contains the mineral cobalt, hence its name cobalamin. This vitamin is primarily responsible for the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system, as well as the formation of red blood cells. It is involved in numerous metabolic pathways, making it an essential nutrient for optimal bodily function.
The human body cannot produce Vitamin B12 on its own, making it an essential nutrient that must be obtained through diet or supplements. Its unique role in the body is often overlooked, but a deficiency can lead to serious health complications. Understanding the importance of Vitamin B12 is the first step towards ensuring optimal health and preventing potential issues.
The Benefits of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 offers a plethora of benefits, contributing to various aspects of our physical and mental health. Let’s explore some of the key advantages of ensuring adequate Vitamin B12 intake.
1. Energy Boost and Metabolism
One of the most well-known benefits of Vitamin B12 is its ability to provide an energy boost. This vitamin plays a crucial role in the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates, helping convert food into energy. It is also involved in the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the body’s primary energy currency. Adequate Vitamin B12 levels can enhance energy production, reduce fatigue, and improve overall stamina.
| Vitamin B12's Role in Energy Production |
|---|
| Metabolism of macronutrients |
| Synthesis of ATP |
| Enhanced energy levels |

2. Cognitive Function and Brain Health
Vitamin B12 is often referred to as the “brain vitamin” due to its crucial role in maintaining cognitive function and overall brain health. It is involved in the production of myelin, a fatty substance that surrounds and protects nerve fibers. This insulation is essential for the efficient transmission of nerve signals, which in turn supports cognitive processes such as memory, concentration, and overall brain function.
Research has also linked Vitamin B12 deficiency to cognitive decline and an increased risk of neurological disorders. Ensuring adequate Vitamin B12 intake can help protect brain health, particularly as we age.
3. Red Blood Cell Formation
Vitamin B12 is an integral part of the process of red blood cell formation. It works alongside other B vitamins, particularly folate, to ensure the proper maturation and division of red blood cells. These cells are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body, and their optimal function is vital for overall health.
A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can lead to a condition called megaloblastic anemia, where red blood cells are abnormally large and unable to function effectively. This can result in fatigue, weakness, and other health complications. By maintaining adequate Vitamin B12 levels, we can support the production of healthy red blood cells and promote optimal oxygen delivery to our tissues.
4. Nervous System Support
As mentioned earlier, Vitamin B12 is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. It helps maintain the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve fibers, ensuring efficient nerve transmission. This is crucial for the proper functioning of our sensory and motor systems, as well as the maintenance of overall nerve health.
Additionally, Vitamin B12 is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that facilitate communication between nerve cells. These neurotransmitters play a key role in mood regulation, sleep patterns, and overall mental well-being. Adequate Vitamin B12 levels can help support a healthy nervous system and promote optimal cognitive and emotional function.
5. DNA Synthesis and Cell Repair
Vitamin B12 is a key player in the process of DNA synthesis and cell repair. It is involved in the methylation cycle, a critical biochemical process that regulates gene expression and ensures the stability of our DNA. This process is essential for the proper functioning and replication of cells, particularly in rapidly dividing tissues such as the skin, hair, and nails.
By supporting DNA synthesis and cell repair, Vitamin B12 contributes to the overall health and vitality of our bodies. It aids in the healing process, helps maintain healthy skin, and promotes the growth of strong hair and nails.
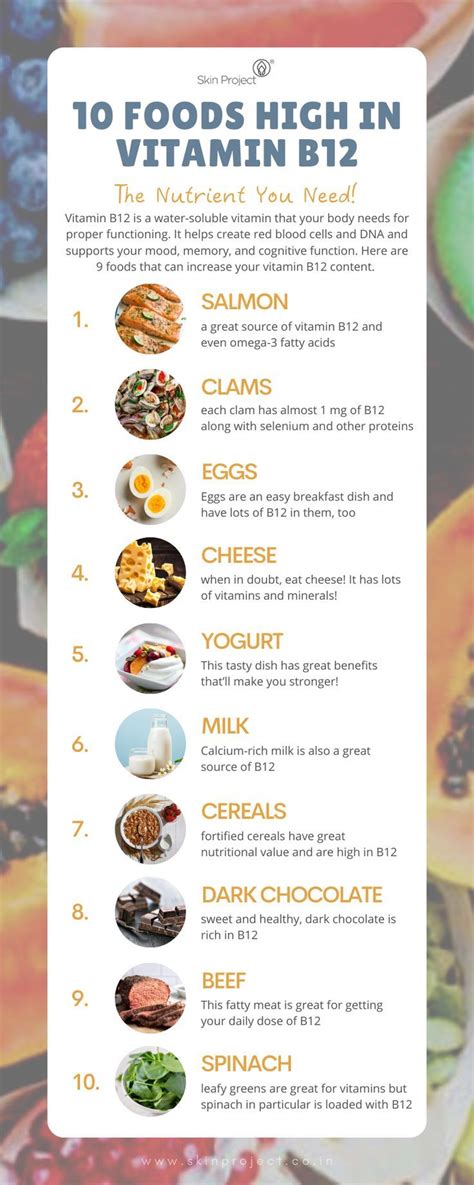
Natural Sources of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal-based foods, making it a challenge for individuals following a vegan or vegetarian diet to obtain adequate amounts. However, there are still several natural sources of Vitamin B12 that can help meet our daily requirements.
Animal-Based Sources
- Meat: Beef, lamb, and pork are excellent sources of Vitamin B12. A 3-ounce serving of beef can provide up to 60% of the daily recommended intake.
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey are also good sources, with a 3-ounce serving providing around 15-20% of the daily requirement.
- Fish and Seafood: Salmon, trout, tuna, and shellfish are rich in Vitamin B12. A 3-ounce serving of cooked salmon, for example, can provide over 100% of the daily recommended intake.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese are decent sources of Vitamin B12. A cup of milk or a serving of yogurt can provide around 15-20% of the daily requirement.
- Eggs: While eggs are a good source of many nutrients, they contain lower amounts of Vitamin B12 compared to other animal products. However, the vitamin is concentrated in the yolk, so consuming whole eggs can still contribute to our daily intake.
Plant-Based Sources
For those following a vegan or vegetarian diet, obtaining Vitamin B12 can be more challenging. While there are no naturally occurring plant-based sources of Vitamin B12, certain foods are fortified with this essential nutrient.
- Fortified Cereals: Many breakfast cereals are fortified with Vitamin B12. Check the nutrition labels to ensure the brand you choose provides a significant amount of the daily value.
- Nutritional Yeast: This inactive yeast, often used as a cheese alternative, is commonly fortified with Vitamin B12. It adds a savory, cheesy flavor to dishes and can be a convenient way to boost Vitamin B12 intake.
- Fortified Plant-Based Milk: Some plant-based milk alternatives, such as soy or almond milk, are fortified with Vitamin B12. Again, check the labels to ensure a sufficient amount is provided.
- Fortified Energy Bars: Certain energy or nutrition bars are specifically formulated for vegetarians and vegans, and they often include Vitamin B12 as part of their nutrient profile.
Vitamin B12 Supplements and Considerations
For individuals who have difficulty meeting their Vitamin B12 needs through diet alone, supplements can be a convenient and effective solution. Vitamin B12 supplements are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, sublingual (under-the-tongue) lozenges, and injections.
Choosing the Right Supplement
When selecting a Vitamin B12 supplement, it is important to consider the form and dosage. Methylcobalamin and cyanocobalamin are the two most common forms of Vitamin B12 supplements. Methylcobalamin is the active form of Vitamin B12 and is more readily utilized by the body, making it a popular choice.
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin B12 varies depending on age, health status, and dietary habits. For adults, the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) is 2.4 micrograms per day. However, certain populations, such as the elderly or those with absorption issues, may require higher doses.
Vitamin B12 and Absorption Issues
Vitamin B12 absorption is a complex process that requires the presence of a protein called intrinsic factor. Some individuals, particularly those with certain medical conditions or those who have had gastrointestinal surgeries, may have difficulty absorbing Vitamin B12 from food or oral supplements. In such cases, sublingual or injectable forms of Vitamin B12 may be more effective.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before starting any supplement regimen, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess your individual needs, recommend appropriate dosages, and monitor your Vitamin B12 levels to ensure optimal health.
FAQs

How much Vitamin B12 do I need daily?
+The recommended daily intake of Vitamin B12 for adults is 2.4 micrograms. However, certain populations may require higher doses. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Can I get enough Vitamin B12 from a vegetarian diet?
+It can be challenging for vegetarians and vegans to obtain sufficient Vitamin B12 from their diet alone. Fortified foods and supplements are often necessary to meet daily requirements.
What are the signs of Vitamin B12 deficiency?
+Symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency can include fatigue, weakness, memory problems, mood changes, and neurological issues. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional.
Can Vitamin B12 supplements cause side effects?
+Vitamin B12 supplements are generally well-tolerated. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as headache, nausea, or allergic reactions. If you experience any adverse effects, consult a healthcare professional.
How long does it take to correct a Vitamin B12 deficiency?
+The time it takes to correct a Vitamin B12 deficiency varies depending on the severity and underlying causes. With proper treatment and supplementation, symptoms often improve within a few weeks, but it may take several months to fully correct the deficiency.



