Typical Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, is a crucial component of our body's energy metabolism, providing the necessary fuel for our cells to function optimally. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is vital for overall health and well-being. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of typical blood sugar levels, offering a detailed understanding of what constitutes healthy glucose concentrations and how these levels can vary throughout the day and under different circumstances.
Understanding Normal Blood Sugar Levels

Normal blood sugar levels refer to the range in which glucose concentrations in the bloodstream are considered healthy and do not pose a risk for diabetes or other metabolic disorders. These levels can fluctuate depending on various factors, including the time of day, recent food intake, and individual metabolic variations.
Fasting Blood Sugar
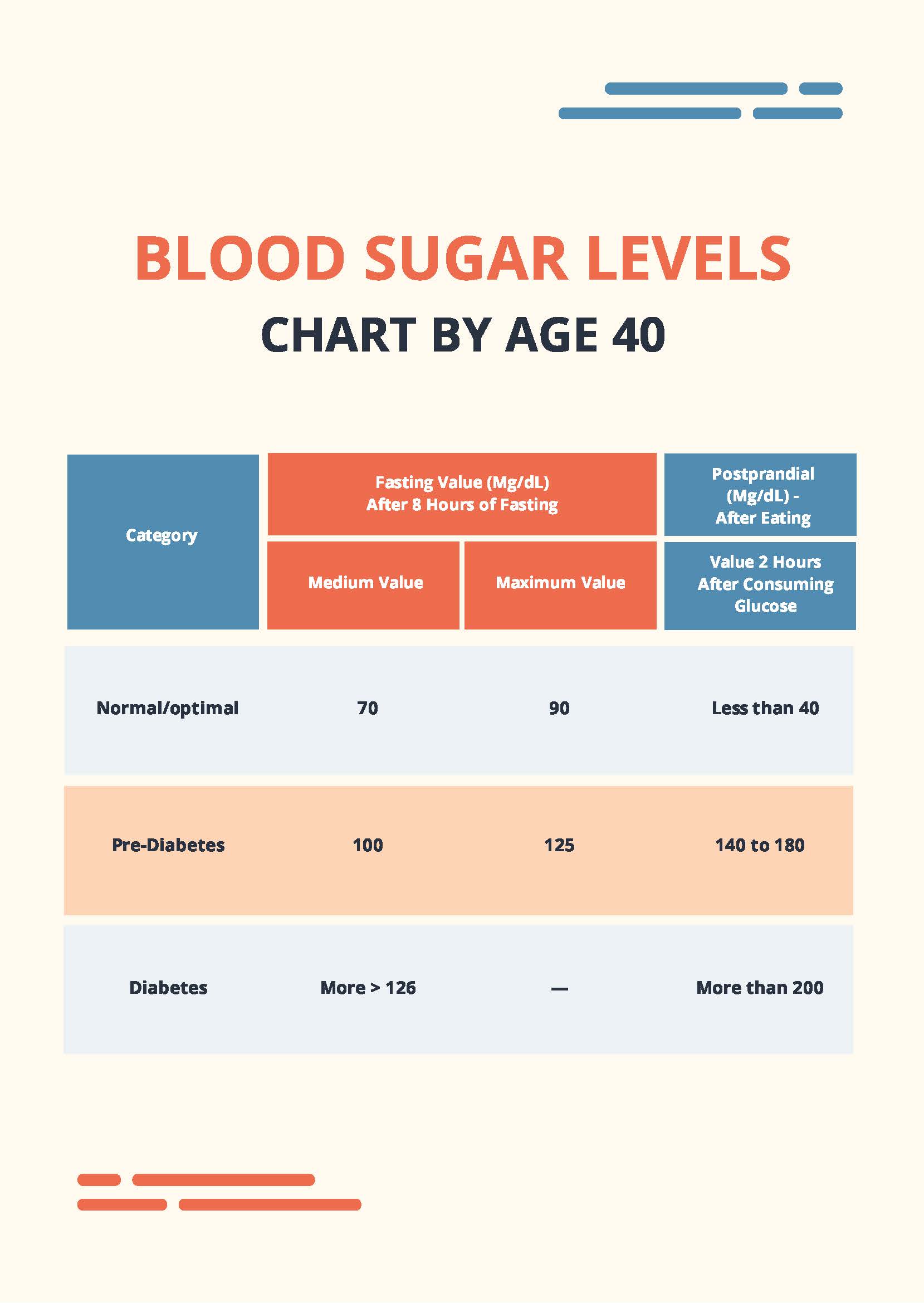
Fasting blood sugar is a measurement taken after an individual has not eaten for at least 8 hours, typically overnight. This is a crucial metric for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association, the following values are considered normal for fasting blood sugar:
| Category | Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Normal | 70–99 |
| Prediabetes | 100–125 |
| Diabetes | ≥126 |

A fasting blood sugar level of 70–99 mg/dL is considered optimal and indicates that the body is effectively regulating glucose levels during periods of fasting.
Postprandial Blood Sugar
Postprandial blood sugar refers to the levels measured two hours after a meal. This metric provides insight into how effectively the body processes and regulates glucose after eating. The normal range for postprandial blood sugar is typically below 140 mg/dL. Consistently elevated postprandial blood sugar levels can be an early indicator of impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes.
Random Blood Sugar
Random blood sugar tests can be conducted at any time of the day, regardless of when the last meal was consumed. These tests are often used to diagnose diabetes when symptoms are present. A random blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher suggests the presence of diabetes, while levels between 140 and 199 mg/dL may indicate prediabetes.
The Impact of Diet and Lifestyle on Blood Sugar

Diet and lifestyle choices play a pivotal role in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Certain foods, particularly those high in refined sugars and simple carbohydrates, can cause rapid spikes in blood glucose, leading to a host of health issues if left unmanaged. On the other hand, a diet rich in complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of diabetes.
Carbohydrate Intake and Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) is a scale that ranks foods based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI are digested rapidly, leading to sharp spikes in blood glucose. Conversely, low-GI foods are digested more slowly, providing a steady release of glucose into the bloodstream. Incorporating more low-GI foods into your diet can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
| Food | Glycemic Index |
|---|---|
| White Bread | 75 |
| Oatmeal | 55 |
| Sweet Potato | 54 |
| Brown Rice | 50 |
It's important to note that the GI value of a food can be influenced by the preparation method and other foods consumed with it. For example, adding healthy fats or proteins to a meal can help lower the overall GI.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is another crucial factor in blood sugar management. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and promoting glucose uptake by muscles. This effect can last for hours after the exercise session, helping to stabilize blood glucose levels throughout the day.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
For individuals with diabetes or prediabetes, managing blood sugar levels is a lifelong endeavor. It involves a combination of dietary modifications, regular physical activity, and, in some cases, medication or insulin therapy. Here are some key strategies for effective blood sugar management:
- Monitor Regularly: Regularly checking blood sugar levels helps individuals understand how their body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. This data is crucial for making informed decisions about diet and lifestyle choices.
- Meal Planning: Planning meals and snacks with a focus on low-GI foods, adequate protein, and healthy fats can help prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar.
- Stay Active: Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines is essential for managing blood sugar. This can include aerobic exercises, strength training, and even simple activities like walking or gardening.
- Medication Adherence: For individuals with diabetes, adhering to prescribed medication regimens is vital. This may include insulin injections, oral medications, or a combination of both.
Future Implications and Innovations
The field of diabetes management and blood sugar control is constantly evolving, with new technologies and treatment modalities on the horizon. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices, for instance, provide real-time data on blood sugar levels, offering a more comprehensive understanding of how the body responds to various factors.
Additionally, advancements in insulin delivery systems, such as smart insulin pens and patches, are making diabetes management more efficient and less invasive. These innovations, coupled with ongoing research into diabetes prevention and cure, offer hope for improved quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar levels?
+
High blood sugar levels, also known as hyperglycemia, can cause a range of symptoms including frequent urination, increased thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds. In severe cases, it can lead to life-threatening complications.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+
The frequency of blood sugar checks depends on individual needs and health status. Individuals with diabetes often need to check their blood sugar levels multiple times a day, especially before and after meals. Those without diabetes may only need to check their fasting blood sugar periodically, typically once a year during routine health checks.
Can stress affect blood sugar levels?
+
Yes, stress can impact blood sugar levels. When the body is under stress, it releases hormones that can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and adequate sleep can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.



