The Allied Countries In Ww2
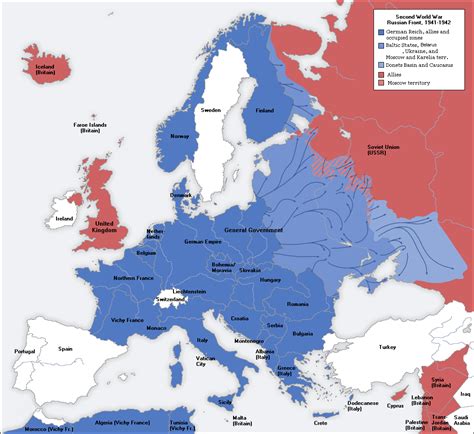
The Second World War, often referred to as WWII, was a global conflict that engulfed nations across the world. Among the participating countries, the Allied forces played a pivotal role in shaping the course of history and ultimately securing victory. This article aims to delve into the depths of this alliance, exploring the countries that formed its backbone and the significant contributions they made to the war effort.
The Formation of the Allied Powers
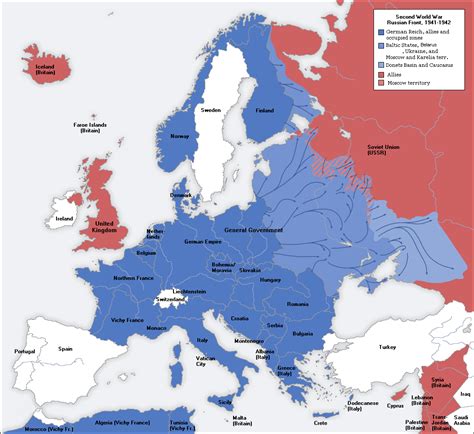
The origins of the Allied alliance can be traced back to the early stages of WWII. On September 1, 1939, Germany's invasion of Poland marked the official start of the war in Europe. In response, two key powers, France and the United Kingdom, declared war on Germany, marking the beginning of a complex alliance that would grow and evolve over the course of the war.
As the war progressed, the Allied forces expanded to include a diverse range of nations, each bringing unique strengths and resources to the fight against the Axis powers. This alliance, though not without its challenges and disagreements, ultimately proved to be a formidable force, characterized by unity and determination.
Key Allied Countries and Their Contributions
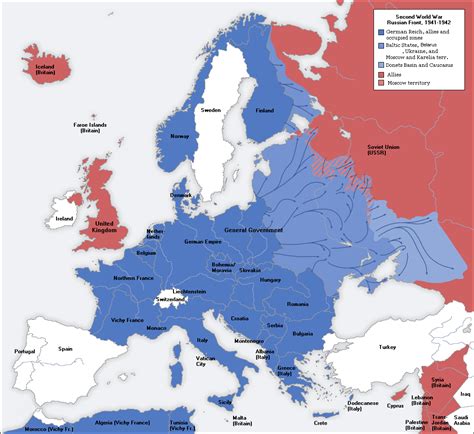
The Allied powers consisted of numerous countries, each playing a crucial role in the war. Here's an in-depth look at some of the key players and their significant contributions:
The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom, often referred to as Britain, was one of the first countries to stand against Germany. With its powerful Royal Navy and a resilient spirit, Britain became a stronghold of resistance. The British forces engaged in fierce battles across Europe, North Africa, and Asia, demonstrating remarkable resilience and tactical prowess.
- Battle of Britain: Perhaps one of the most iconic moments in British history, the Battle of Britain showcased the nation's air defense capabilities. The Royal Air Force, with its Spitfire and Hurricane fighters, thwarted the German Luftwaffe's bombing campaigns, a pivotal moment that prevented Germany from gaining air superiority.
- D-Day Preparations: The United Kingdom played a vital role in the planning and execution of the D-Day landings. British engineers and scientists developed innovative technologies, such as the Mulberry Harbours, which provided vital port facilities for the Allied invasion force.
- Resistance and Intelligence: Britain's intelligence services, including the famous codebreakers at Bletchley Park, played a crucial role in deciphering German Enigma codes, providing invaluable intelligence to the Allied forces.
The United States of America
The United States entered the war following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. With its vast resources and industrial might, the US became a pivotal force in the Allied alliance. The American military, known for its logistical prowess and technological advancements, made significant contributions on both the European and Pacific fronts.
- The Arsenal of Democracy: President Franklin D. Roosevelt's famous phrase aptly described the US's role in supplying the Allied forces with arms, ammunition, and other vital resources. The US became the primary supplier, ensuring a steady flow of military equipment to the war zones.
- Normandy Landings: The US played a leading role in the D-Day landings, with the US Army and Navy coordinating the massive invasion of Normandy. The US 1st and 29th Infantry Divisions, alongside other units, stormed the beaches, a pivotal moment in the liberation of Europe.
- Pacific Theatre: In the Pacific, the US Navy and Marine Corps engaged in fierce battles against the Japanese Imperial Navy. The US fleet, with its aircraft carriers and battleships, played a crucial role in turning the tide of the war in the Pacific, culminating in the decisive Battle of Midway.
The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union, a vast nation spanning across Eurasia, made an immense contribution to the Allied victory. Despite initially signing a non-aggression pact with Germany, the Soviet Union found itself under attack in 1941, leading to a fierce and protracted war on the Eastern Front.
- The Great Patriotic War: The Soviet people endured immense suffering and loss during the war. The Red Army, with its vast numbers and unwavering determination, engaged in some of the largest and bloodiest battles in history, including the Battle of Stalingrad and the Battle of Kursk.
- Industrial Relocation: The Soviet leadership demonstrated remarkable strategic thinking by relocating key industries to the eastern regions, away from the advancing German forces. This ensured that the Soviet war machine continued to produce vital weaponry and equipment despite the occupation of western territories.
- Partisan Resistance: The Soviet Union's partisan forces played a crucial role in disrupting German supply lines and gathering intelligence. These brave men and women operated behind enemy lines, striking fear into the hearts of the occupying forces.
China
China, a country already embroiled in conflict with Japan prior to WWII, became an integral part of the Allied alliance. The Chinese resistance against Japanese aggression played a crucial role in diverting Japanese resources and attention, ultimately contributing to the Allied victory.
- Sino-Japanese War: The Second Sino-Japanese War, which began in 1937, saw China engage in a protracted struggle against Japan. The Chinese resistance, though facing significant challenges, managed to hold their ground, preventing Japan from achieving its imperialist ambitions.
- Burma Road: The Burma Road, a vital supply route, played a crucial role in supplying China with essential war materials. The road, constructed through rugged terrain, connected China to British-controlled Burma, ensuring a steady flow of resources to the Chinese war effort.
- Strategic Importance: China's resistance against Japan not only tied down a significant portion of the Japanese military but also provided a staging ground for the Allied forces to launch counterattacks in the Pacific. The Chinese theater of war proved to be a crucial factor in the overall Allied strategy.
The Power of Unity
The Allied alliance during WWII was a testament to the power of unity and cooperation. Despite their differences, these nations came together to fight a common enemy, often overcoming tremendous odds and adversity. The contributions of each country were unique and indispensable, highlighting the importance of collective effort in achieving a greater goal.
| Country | Key Contributions |
|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Resilience, Air Defense, Technological Innovations |
| United States | Industrial Might, Normandy Landings, Pacific Campaigns |
| Soviet Union | Enormous Sacrifice, Strategic Thinking, Partisan Resistance |
| China | Resistance, Supply Route, Diversion of Japanese Forces |

Frequently Asked Questions
How many countries were part of the Allied powers during WWII?
+The Allied powers consisted of over 50 countries, each contributing in unique ways to the war effort. This alliance included major powers like the United Kingdom, United States, Soviet Union, and China, as well as smaller nations across Europe, Asia, and Africa.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What was the significance of the D-Day landings in the Allied victory?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The D-Day landings, codenamed Operation Overlord, were a pivotal moment in the war. It marked the beginning of the liberation of Western Europe from Nazi occupation. The successful execution of this complex operation opened a second front, stretching German resources and ultimately leading to their defeat.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How did the Soviet Union's partisan forces impact the war?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The Soviet partisan forces, operating behind enemy lines, played a crucial role in disrupting German supply lines and gathering intelligence. Their actions tied down significant German resources, hindered military operations, and provided valuable information to the Red Army.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What role did China play in the Allied alliance?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>China's resistance against Japanese aggression was crucial in the overall Allied strategy. By diverting Japanese forces and resources, China provided a strategic advantage to the Allied powers, especially in the Pacific theater. The Sino-Japanese War also tied down a significant portion of the Japanese military, preventing them from focusing solely on the Pacific.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
The Allied countries during WWII exemplified the strength that comes from unity and cooperation. Their collective efforts, despite differences and challenges, led to a victory that reshaped the world. The legacy of their sacrifices and achievements continues to inspire and guide us today.