Hiv Mean
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a significant global health concern, impacting millions of lives worldwide. Understanding what HIV means, its implications, and the progress made in combating this virus is crucial for raising awareness and promoting effective prevention and treatment strategies.
The Basics of HIV: An Overview

HIV is a lentivirus, a subtype of retrovirus, that causes HIV infection and, if left untreated, progresses to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). This virus specifically targets the immune system, primarily affecting CD4+ T cells, a type of white blood cell essential for fighting off infections and diseases.
HIV can be transmitted through various bodily fluids, including blood, semen, pre-seminal fluid, rectal fluids, vaginal fluids, and breast milk. The most common modes of transmission are through unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing contaminated needles or syringes, and from an HIV-positive mother to her child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
The Impact of HIV Infection

When HIV enters the body, it begins to replicate rapidly, integrating its genetic material into the host’s DNA. Over time, the virus progressively weakens the immune system, leading to a decline in the number of CD4+ T cells. As the immune system weakens, the body becomes increasingly vulnerable to a wide range of infections and diseases, known as opportunistic infections, which can be life-threatening.
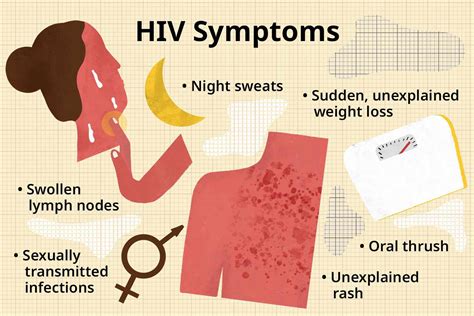
The progression of HIV infection is typically categorized into three stages: acute infection, chronic or asymptomatic infection, and AIDS. During the acute infection stage, individuals may experience flu-like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. However, many people do not display any symptoms, making early detection challenging.
If left untreated, HIV infection progresses to the chronic stage, where the virus continues to replicate, causing a gradual decline in CD4+ T cell count. This stage can last for several years, and individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms or health issues. However, without proper treatment, the immune system eventually becomes severely compromised, leading to the development of AIDS.
AIDS, the most advanced stage of HIV infection, is characterized by a significant drop in CD4+ T cell count and the presence of opportunistic infections or cancers. At this stage, the immune system is severely damaged, making it difficult for the body to fight off even common infections and illnesses.
Treatment and Management of HIV
The good news is that HIV is a manageable condition with the right treatment and care. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is the primary treatment for HIV, and it has revolutionized the management of this virus. ART involves a combination of medications that work to prevent the virus from replicating, reducing the viral load in the body and allowing the immune system to recover and strengthen.
Early diagnosis and timely initiation of ART are crucial for effective HIV management. When started promptly, ART can significantly slow down the progression of the disease, enabling individuals to lead long and healthy lives. Moreover, effective treatment can reduce the viral load to undetectable levels, making it highly unlikely for HIV to be transmitted to others.
In addition to ART, comprehensive HIV care includes regular medical check-ups, monitoring of CD4+ T cell count and viral load, and access to support services. This holistic approach ensures that individuals living with HIV receive the necessary medical, psychological, and social support to manage their condition and maintain their overall well-being.
Prevention and Education: Key Strategies
Preventing the transmission of HIV is vital to controlling the spread of the virus and protecting public health. Education plays a pivotal role in HIV prevention, empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to protect themselves and their partners.
Key prevention strategies include practicing safer sex, such as using condoms consistently and correctly, and avoiding the sharing of needles or other equipment for injecting drugs. Regular HIV testing is also essential, allowing individuals to know their status and take appropriate steps if they test positive.
For those at higher risk of HIV infection, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is an effective prevention tool. PrEP involves taking a daily pill containing antiretroviral medications, which can significantly reduce the risk of acquiring HIV. Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is another option, which involves taking antiretroviral medications as soon as possible after potential exposure to HIV, to prevent infection.
Community engagement and awareness campaigns are crucial in promoting HIV prevention and reducing stigma. By fostering open conversations about HIV, providing accurate information, and offering support to those affected, communities can create an environment that encourages testing, treatment, and overall HIV acceptance.
Global Efforts and Progress

The global response to HIV has led to significant advancements in treatment, prevention, and advocacy. Over the years, numerous international organizations, governments, and healthcare providers have joined forces to combat HIV, resulting in improved access to testing, treatment, and support services.
| Key Global Initiatives | Impact |
|---|---|
| The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria | Provided financial resources to support HIV programs and research worldwide, leading to improved access to ART and reduced HIV-related deaths. |
| Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) | Coordinated global efforts, set targets, and monitored progress towards achieving HIV-related goals, such as increasing access to treatment and reducing new HIV infections. |
| World Health Organization (WHO) HIV Guidelines | Offered evidence-based guidance on HIV prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and care, ensuring that healthcare providers and policymakers have the latest information to inform their practices. |

These initiatives, along with dedicated research efforts, have led to the development of more effective and accessible antiretroviral medications, improved diagnostic tools, and innovative prevention strategies. As a result, the number of HIV-related deaths has declined significantly, and the quality of life for people living with HIV has improved.
Looking Towards the Future
While significant progress has been made in the fight against HIV, challenges remain. Stigma and discrimination continue to impact those living with HIV, hindering their access to healthcare and support. Additionally, HIV continues to disproportionately affect certain populations, such as men who have sex with men, transgender individuals, people who inject drugs, and individuals from marginalized communities.
However, with continued global efforts, increased investment in research, and a commitment to equity and human rights, it is possible to envision a future where HIV is no longer a global health concern. By combining effective prevention strategies, early diagnosis, and timely treatment, we can strive towards an AIDS-free generation and a world where HIV is a manageable condition.
How is HIV transmitted?
+HIV can be transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing contaminated needles or syringes, and from an HIV-positive mother to her child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
What is the difference between HIV and AIDS?
+HIV is the virus that causes HIV infection. If left untreated, HIV can progress to AIDS, which is the most advanced stage of HIV infection, characterized by a severely compromised immune system and the presence of opportunistic infections.
How can I protect myself from HIV?
+Practicing safer sex, such as using condoms, and avoiding the sharing of needles or other equipment for injecting drugs are effective ways to reduce the risk of HIV transmission. Regular HIV testing is also crucial for early detection and timely treatment.
What is the role of antiretroviral therapy (ART) in HIV management?
+ART is the primary treatment for HIV, and it involves a combination of medications that prevent the virus from replicating. By taking ART consistently, individuals can reduce their viral load, strengthen their immune system, and lead a healthy life.
How can we address HIV-related stigma and discrimination?
+Community engagement, education, and advocacy play crucial roles in combating HIV-related stigma. By fostering open conversations, providing accurate information, and promoting empathy and understanding, we can create a supportive environment for those living with HIV.



