Glucose Drink Test

The Glucose Drink Test, also known as the Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT), is a vital diagnostic tool used to assess an individual's glucose metabolism and detect potential issues related to blood sugar regulation. This non-invasive test plays a crucial role in the early identification of conditions like diabetes and metabolic disorders, offering valuable insights into an individual's overall health.
The process involves consuming a glucose drink and subsequently monitoring blood sugar levels over a specified period, typically two hours. The results provide healthcare professionals with detailed information about how the body processes glucose, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various health conditions.
In this comprehensive article, we delve into the intricacies of the Glucose Drink Test, exploring its purpose, procedure, interpretation of results, and its significance in modern healthcare. By understanding the science behind this test, we can appreciate its critical role in preventive medicine and the management of metabolic disorders.
Understanding the Glucose Drink Test
The Glucose Drink Test is a fundamental tool in endocrinology and diabetes management, providing a window into the body’s glucose metabolism. It is particularly valuable in the early detection and management of conditions like diabetes, prediabetes, and gestational diabetes, offering a proactive approach to healthcare.
The Purpose of the Test
The primary objective of the Glucose Drink Test is to evaluate how the body handles glucose, a simple sugar that serves as a primary source of energy for the body. By administering a controlled dose of glucose and monitoring the body’s response, healthcare professionals can assess the efficiency of glucose metabolism and identify potential abnormalities.
This test is particularly crucial for individuals with a higher risk of developing diabetes, such as those with a family history of the disease, overweight individuals, and women who have had gestational diabetes during pregnancy. Early detection through the Glucose Drink Test allows for timely intervention and management, reducing the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes.
How the Test Works
The Glucose Drink Test is a simple and straightforward procedure, typically conducted in a clinical setting. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
- Preparation: The individual is required to fast for a specific period, usually overnight or for at least 8-10 hours, to ensure an accurate baseline measurement.
- Blood Sample Collection: Before consuming the glucose drink, a blood sample is taken to measure the fasting blood glucose level. This provides a reference point for comparison.
- Glucose Drink Administration: The individual is then given a drink containing a known amount of glucose, typically 75 grams for adults. This drink is designed to rapidly increase blood glucose levels.
- Post-Glucose Monitoring: After consuming the drink, the individual's blood glucose levels are monitored at specific intervals, typically at 30-minute, 1-hour, and 2-hour marks. Additional samples may be taken depending on the protocol.
- Blood Sample Analysis: The blood samples collected at each interval are analyzed to determine the glucose levels at those specific times.
Interpreting the Results

The interpretation of Glucose Drink Test results is a critical step in diagnosing and managing metabolic disorders. Healthcare professionals analyze the blood glucose levels at each interval to determine the body’s response to the glucose load.
Normal Response
In a normal response, the individual’s blood glucose levels will rise after consuming the glucose drink but will return to the fasting level within the standard time frame. This indicates that the body is effectively managing glucose metabolism.
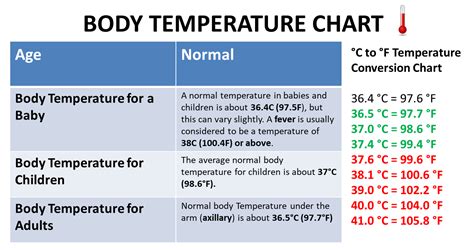
Here's a simplified table illustrating the expected blood glucose levels for a normal response:
| Time | Blood Glucose Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Fasting | 70-99 |
| 30 minutes | 120-180 |
| 1 hour | 140-200 |
| 2 hours | 70-140 |

Note: The exact values may vary slightly depending on the laboratory reference ranges and individual health factors.
Abnormal Responses
Abnormal responses in the Glucose Drink Test can indicate various metabolic disorders, including diabetes and prediabetes. Here are some common abnormal responses and their potential implications:
- Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT): This occurs when the blood glucose levels are higher than normal but do not reach diabetic levels. It indicates a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes and may require lifestyle modifications and regular monitoring.
- Diabetes Mellitus: If the blood glucose levels remain elevated throughout the test, especially if they exceed 200 mg/dL at the 2-hour mark, it is indicative of diabetes. Further diagnostic tests and immediate management are necessary.
- Gestational Diabetes: Pregnant women may undergo a modified version of the Glucose Drink Test to screen for gestational diabetes. Higher-than-normal blood glucose levels at any interval may suggest the presence of gestational diabetes, requiring specialized care during pregnancy.
Significance and Future Implications
The Glucose Drink Test holds immense significance in the field of preventive medicine. By identifying metabolic disorders at an early stage, healthcare professionals can implement interventions that may delay or even prevent the onset of diabetes and its associated complications.
Furthermore, the test's ability to detect prediabetes allows individuals to make lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthier diet and increasing physical activity, which can significantly reduce the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes. This proactive approach to health management can lead to improved quality of life and reduced healthcare costs.
In the future, advancements in glucose monitoring technology may further enhance the accuracy and convenience of the Glucose Drink Test. Continuous glucose monitoring devices, for instance, could provide real-time data during the test, offering more detailed insights into an individual's glucose metabolism.
Additionally, with the increasing focus on personalized medicine, the Glucose Drink Test may be tailored to individual risk factors and genetic predispositions, allowing for more precise predictions and interventions.
Conclusion
The Glucose Drink Test is a cornerstone of diabetes diagnosis and management, offering a non-invasive and effective method to assess glucose metabolism. By understanding the procedure, interpreting results, and recognizing its significance, we can appreciate the vital role this test plays in modern healthcare.
As our understanding of metabolic disorders advances and technology continues to evolve, the Glucose Drink Test will likely remain a crucial tool in the early detection and management of diabetes, paving the way for improved health outcomes and a brighter future for those at risk.
How often should the Glucose Drink Test be performed?
+The frequency of the Glucose Drink Test depends on individual risk factors and health status. For those at higher risk, such as individuals with a family history of diabetes or those who are overweight, it is recommended to undergo the test every 3 years starting at age 45. For women who have had gestational diabetes, it is advised to have the test annually. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend more frequent testing, especially if there are concerns about developing diabetes.
Can the Glucose Drink Test diagnose type 1 diabetes?
+The Glucose Drink Test is primarily used to diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed based on symptoms, such as frequent urination, excessive thirst, and weight loss, along with high blood glucose levels. However, in certain cases, the Glucose Drink Test can be used to confirm the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes, especially in individuals who present with high blood glucose levels and no known risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Are there any risks associated with the Glucose Drink Test?
+The Glucose Drink Test is generally safe and well-tolerated. However, some individuals may experience side effects such as nausea, bloating, or mild headaches after consuming the glucose drink. These symptoms are usually temporary and resolve on their own. In rare cases, severe allergic reactions may occur, but this is extremely uncommon. It is important to discuss any concerns or potential risks with your healthcare provider before undergoing the test.