Blood Sugar Level Meaning
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being, as it directly impacts our energy levels, cognitive function, and long-term health outcomes. Understanding what blood sugar levels mean and how they affect our bodies is essential for managing diabetes and promoting overall metabolic health.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of blood sugar levels, exploring their significance, the factors that influence them, and the implications they have on our daily lives. By the end, you'll have a deeper understanding of this vital aspect of human physiology and how to keep your blood sugar levels in check.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels: A Crucial Metabolic Marker
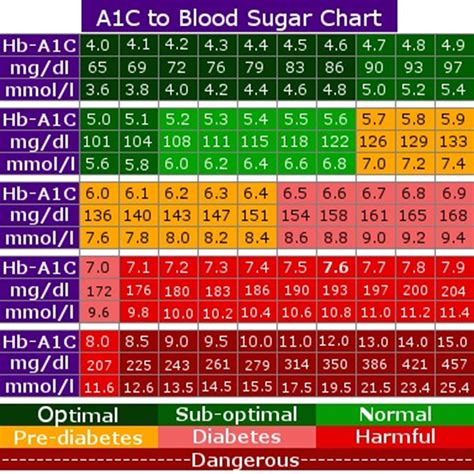
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for our bodies. It's derived from the foods we eat, particularly carbohydrates, and is essential for fueling our cells, tissues, and organs. The body tightly regulates blood sugar levels to ensure they remain within a healthy range, as both high and low blood sugar can lead to adverse health effects.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels: The Optimal Range
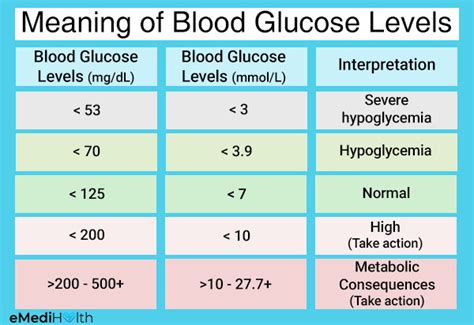
For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically within the following ranges:
| Time of Measurement | Normal Range (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Fasting (before meals) | 70–99 |
| Postprandial (2 hours after a meal) | < 140 |
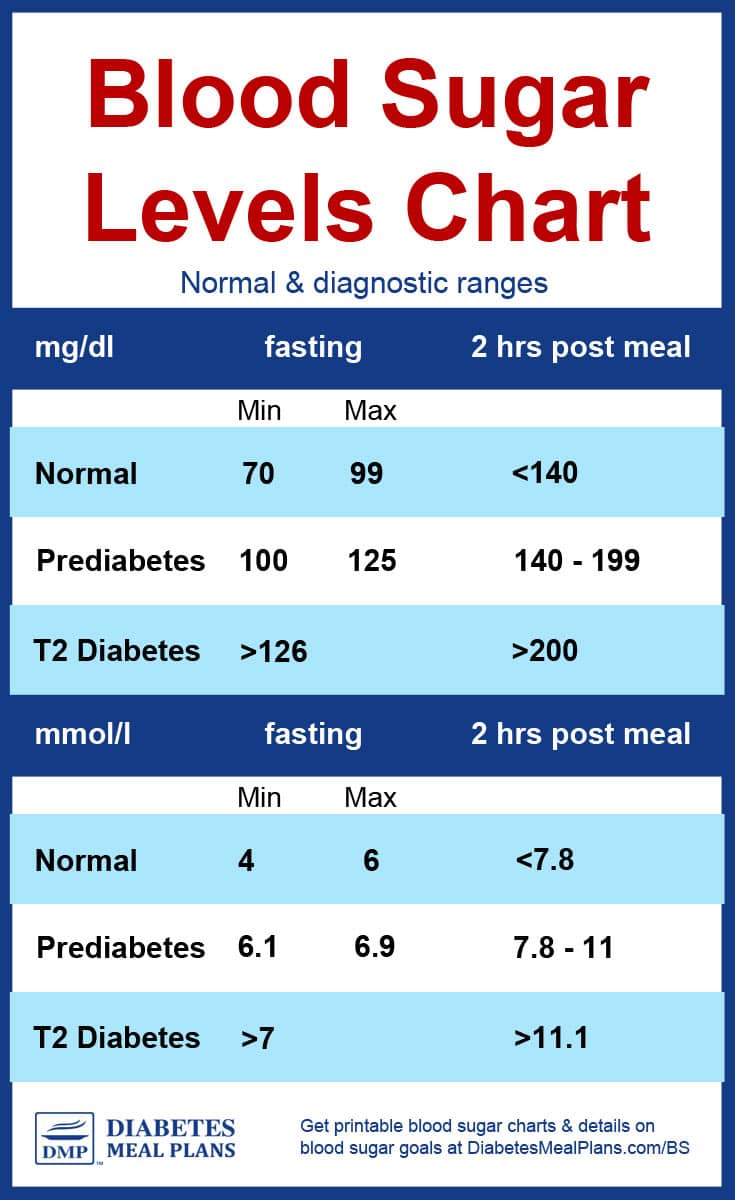
These values may vary slightly based on individual factors and the specific laboratory or testing method used. However, they provide a general guideline for what constitutes a healthy blood sugar level.
The Impact of High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)
When blood sugar levels consistently exceed the normal range, it's known as hyperglycemia. This can occur due to various factors, including:
- Insulin Resistance: The body's cells become less responsive to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar. This is a common feature of type 2 diabetes.
- Pancreatic Issues: Conditions affecting the pancreas, such as pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer, can impair insulin production.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can contribute to insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels.
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a diet high in refined carbohydrates and added sugars can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar.
Chronic hyperglycemia can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): A life-threatening condition where the body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones.
- Cardiovascular Disease: High blood sugar is a risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Prolonged hyperglycemia can damage nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Kidney Damage (Nephropathy): The kidneys may become damaged over time, potentially leading to kidney failure.
- Eye Problems: Hyperglycemia can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision issues and even blindness.
The Dangers of Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
On the other end of the spectrum, low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, occurs when glucose levels drop below the normal range. This can happen due to various reasons, including:
- Diabetes Medications: Certain medications used to treat diabetes, such as insulin or sulfonylureas, can lower blood sugar too much.
- Skipping Meals: Going too long without eating can deplete glucose stores.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can interfere with glucose metabolism and cause hypoglycemia.
- Intense Exercise: Strenuous physical activity can rapidly deplete glucose stores.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia include dizziness, trembling, confusion, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent serious complications.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and underlying health conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for managing blood sugar effectively.
Diet and Blood Sugar
The foods we eat have a direct impact on blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates, which are broken down into glucose, have the most significant effect. Simple carbohydrates, like those found in sugary drinks and desserts, are rapidly absorbed, leading to quick spikes in blood sugar. Complex carbohydrates, such as those in whole grains and legumes, are digested more slowly, providing a steadier source of glucose.
Protein and healthy fats can also play a role in blood sugar management. Including protein and healthy fats in meals can help slow the absorption of glucose, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar.
Physical Activity and Blood Sugar
Regular physical activity is beneficial for blood sugar control. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to utilize glucose more efficiently. It also helps burn excess glucose, reducing blood sugar levels. However, intense exercise can lead to a temporary drop in blood sugar, so it's important to monitor levels before and after physical activity, especially for individuals with diabetes.
Stress and Blood Sugar
Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels. When we're stressed, our bodies release hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause blood sugar to rise. Chronic stress can lead to consistently elevated blood sugar levels and contribute to insulin resistance.
Health Conditions and Medications
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, pancreatitis, and certain hormonal disorders, can directly affect blood sugar levels. Additionally, certain medications, including steroids and some diuretics, can impact glucose metabolism and blood sugar regulation.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels: Strategies and Tips
Whether you have diabetes or are looking to optimize your metabolic health, there are numerous strategies you can employ to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Dietary Approaches
A well-balanced diet is key to maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Here are some dietary strategies to consider:
- Carbohydrate Counting: Understanding the carbohydrate content of your meals and snacks can help you better manage blood sugar. Aim for a consistent carbohydrate intake throughout the day.
- Low Glycemic Index (GI) Foods: Choosing low GI foods, which are digested more slowly, can help prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar. Examples include whole grains, legumes, and most fruits and vegetables.
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber, particularly soluble fiber, can slow the absorption of glucose and help regulate blood sugar levels. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet.
- Protein and Healthy Fats: Including protein and healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, and avocado, can help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote satiety.
- Portion Control: Paying attention to portion sizes can help prevent overeating and excessive glucose intake.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to dietary changes, the following lifestyle modifications can also help manage blood sugar levels:
- Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. This can include activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Stress Management: Incorporate stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough quality sleep is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Aim for 7–9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night.
- Weight Management: For individuals with obesity or overweight, losing weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for individuals with diabetes and those at risk. This allows you to track your blood sugar levels, identify patterns, and make necessary adjustments to your diet and lifestyle. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate monitoring schedule and target blood sugar ranges for your specific situation.
The Future of Blood Sugar Management: Emerging Technologies and Trends
Advancements in technology and medical research are continually improving blood sugar management for individuals with diabetes. Here are some of the most promising developments on the horizon:
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Devices
CGM devices provide real-time blood sugar readings, offering a more comprehensive understanding of glucose trends throughout the day. These devices can alert users to high or low blood sugar levels, helping them make timely adjustments.
Artificial Pancreas Systems
Also known as closed-loop insulin delivery systems, these devices combine CGM technology with an insulin pump. They automatically adjust insulin delivery based on real-time blood sugar readings, mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas.
Precision Medicine Approaches
Researchers are developing personalized diabetes management strategies based on individual genetic, metabolic, and environmental factors. This approach aims to optimize treatment plans for each person, improving outcomes and quality of life.
Cell-Based Therapies
Stem cell-based therapies and pancreatic islet cell transplantation are being explored as potential cures for type 1 diabetes. These approaches aim to restore insulin production and regulate blood sugar levels naturally.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Blood Sugar Health
Understanding and managing blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health and well-being. By adopting a balanced diet, incorporating regular physical activity, and making other healthy lifestyle choices, you can effectively manage your blood sugar and reduce your risk of diabetes-related complications.
Stay informed, monitor your blood sugar regularly, and consult with healthcare professionals to ensure you're on the right track. With the right strategies and tools, you can take control of your blood sugar health and live a vibrant, fulfilling life.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia)?
+Symptoms of hyperglycemia include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and weight loss. If left untreated, it can lead to more severe complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and cardiovascular disease.
How can I lower my blood sugar quickly if it’s too high?
+If your blood sugar is high, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice. Generally, strategies like drinking plenty of water, engaging in light physical activity, and reducing carbohydrate intake can help lower blood sugar levels.
What are some healthy snacks for managing blood sugar levels?
+Healthy snacks that can help manage blood sugar include nuts and seeds, plain yogurt with berries, apple slices with almond butter, and vegetable sticks with hummus. These snacks provide a balance of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats, which can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
How does stress impact blood sugar levels?
+Stress can increase blood sugar levels by triggering the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can cause insulin resistance and impair glucose metabolism. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and regular exercise can help maintain healthier blood sugar levels.


