Anxiety Anxiety

Anxiety is a common mental health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a complex and often misunderstood condition, with a range of symptoms and manifestations. Understanding anxiety and its impact is crucial, as it can significantly influence an individual's daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the depths of anxiety, exploring its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and strategies for managing this pervasive condition.
Unraveling the Complexities of Anxiety

Anxiety disorders are a group of related conditions that can cause excessive worry, fear, and nervousness. These feelings can be overwhelming and interfere with daily activities, work, and personal relationships. While it is normal to experience some anxiety in certain situations, such as before an important event or during a stressful period, anxiety disorders go beyond the typical anxiety we all experience.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), a widely recognized guide in the field of mental health, categorizes several types of anxiety disorders, each with its own unique characteristics and symptoms. These include:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Characterized by excessive and uncontrollable worry about various aspects of life, including work, social interactions, health, and everyday routine activities.
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Individuals with this disorder experience intense fear and anxiety in social situations, often fearing scrutiny or embarrassment.
- Panic Disorder: This condition involves recurrent panic attacks, which are sudden and intense episodes of fear accompanied by physical symptoms such as rapid heart rate, shortness of breath, and trembling.
- Specific Phobias: These are intense fears of specific objects or situations, such as heights, flying, or certain animals.
- Agoraphobia: Often linked to panic disorder, agoraphobia involves fear and avoidance of places or situations where escape might be difficult, such as crowded areas or public transportation.
- Separation Anxiety Disorder: Commonly associated with children, but can also affect adults, this disorder involves excessive anxiety related to separation from certain people or places that provide a sense of safety.
Each of these disorders has its own set of diagnostic criteria and unique challenges. It's important to note that individuals can experience more than one type of anxiety disorder simultaneously, and the symptoms can vary greatly from person to person.
Unveiling the Symptoms: Recognizing Anxiety
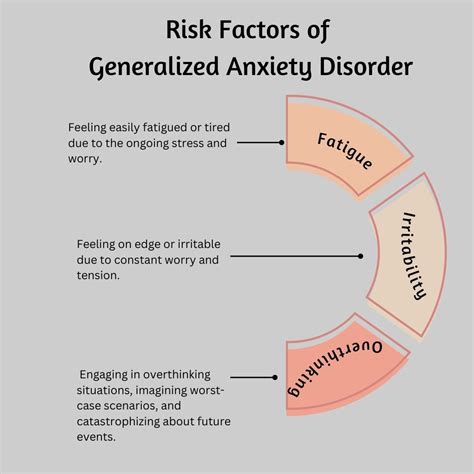
Anxiety disorders can manifest in various ways, and the symptoms can be both physical and psychological. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention and effective management.
Physical Symptoms
The physical symptoms of anxiety can be quite pronounced and often resemble those of a panic attack. These may include:
- Rapid heart rate or palpitations
- Shortness of breath or a feeling of choking
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Nausea or stomach problems
- Sweating
- Trembling or shaking
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Headaches
- Fatigue or muscle tension
These physical symptoms can be distressing and may lead individuals to seek medical attention, only to find that their physical health is not the primary concern.
Psychological Symptoms
The psychological symptoms of anxiety can be just as debilitating. They often involve excessive worry, fear, and nervousness, but can also manifest in other ways, such as:
- Restlessness or feeling on edge
- Difficulty concentrating or focusing
- Irritability or mood swings
- Avoidance of certain situations or activities
- Intrusive thoughts or mental images
- Feeling detached from oneself or one's surroundings (derealization)
- Fear of losing control or going crazy
These psychological symptoms can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, leading to social withdrawal, difficulty in maintaining relationships, and even impaired work or academic performance.
Treatment Options: Navigating the Path to Relief
Fortunately, there are various treatment options available for anxiety disorders, and effective management is possible. The choice of treatment often depends on the type and severity of the anxiety disorder, as well as individual preferences and circumstances.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, or talk therapy, is a cornerstone of anxiety disorder treatment. Various types of psychotherapy have proven effective, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. It teaches coping strategies and provides tools to manage anxiety symptoms.
- Exposure Therapy: This approach gradually exposes individuals to the situations or objects they fear, helping them learn to manage their anxiety in a safe and controlled environment.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT combines elements of CBT with mindfulness practices, focusing on emotion regulation and interpersonal effectiveness.
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT): ACT emphasizes accepting difficult thoughts and emotions while committing to taking actions aligned with personal values.
Psychotherapy can be provided individually or in group settings, depending on the individual's needs and preferences.
Medication
Medication is another common treatment approach for anxiety disorders. Several types of medications can be prescribed, including:
- Antidepressants: These medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), are often used to treat anxiety disorders. They work by altering the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain.
- Benzodiazepines: These medications provide quick relief from anxiety symptoms but are generally used on a short-term basis due to the risk of dependence.
- Beta-Blockers: Often used to treat physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heart rate and trembling.
- Antipsychotics: In some cases, antipsychotic medications may be prescribed for severe anxiety disorders or when other treatments have not been effective.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate medication and dosage, as well as to monitor potential side effects.
Lifestyle Interventions
In addition to psychotherapy and medication, lifestyle interventions can play a significant role in managing anxiety disorders. These may include:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity has been shown to reduce anxiety symptoms and improve overall well-being. Activities such as yoga, tai chi, and aerobic exercise can be particularly beneficial.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in nutrients can support mental health. Foods containing omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish and nuts, have been linked to reduced anxiety symptoms.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practices like meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help individuals manage stress and reduce anxiety.
- Social Support: Building a strong support network and maintaining healthy relationships can provide emotional support and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can improve sleep quality, which is essential for managing anxiety.
Combining these lifestyle interventions with professional treatment can enhance the effectiveness of anxiety management.
Conclusion: A Path Towards Healing
Anxiety disorders are complex and can significantly impact an individual’s life. However, with proper understanding, effective treatment, and supportive strategies, it is possible to manage and overcome these challenges. Seeking help from healthcare professionals and implementing self-care practices can lead to a path of healing and improved well-being.
Remember, you are not alone in your journey, and there is hope for a brighter and more peaceful future.
What are some common triggers for anxiety attacks?
+Anxiety attacks can be triggered by various factors, including stress, traumatic events, certain phobias, social situations, or even physical health issues. Identifying personal triggers is an essential step in managing anxiety.
Can anxiety disorders be cured completely?
+While anxiety disorders are treatable, they are often considered chronic conditions. However, with effective management and treatment, individuals can achieve significant symptom relief and improve their quality of life.
How long does it take to see improvements with anxiety treatment?
+The timeline for improvement varies for each individual. Some may experience relief within a few weeks, while others may take several months. Consistency in treatment and a commitment to self-care practices are key to long-term success.



